When a company decides to introduce new technology to its operations, they’re also introducing new digital security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals will try to prey upon. As a result, there is rapid growth in the cybersecurity market. ABI Research forecasts that, compared to the 75,000 Hardware Security Module (HSM) shipments in 2021, there will be 125,000 shipments in 2026. Much of the attention is being paid to industrial cybersecurity and manufacturing security. From protecting customer payment credentials to supply chain telematics, cybersecurity is one of the most important aspects of the modern business and there are a few trends worth watching.
Cybersecurity on the Industrial Front
As industrial operators shift to Industry 4.0, security implementations will address various aspects of manufacturing and the supply chain, including audits, due diligence, third-party risk management, and firmware Over-the-Air (OTA) updates. Some of the biggest drivers for investment in industrial cybersecurity include asset visibility tracking, supply chain governance, and the appealing features of emerging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) solutions. Some of those features include the following:
- Fast user switching
- Hot patching
- Industrial Control System (ICS) cloudification
- Network probes
- Secured Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) programming
Critical infrastructure sectors, such as energy, transport, and water & waste management are going all-in with digital security. By the end of 2022, cybersecurity spending across these three industries will reach US$23 billion and grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10% through 2027. All in all, cybersecurity is largely seen by industrial operators as a critical step in the process of deploying more connected devices and will be in great demand through the forecast period.
Chart 1: Industrial Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity Spending by Sector: 2022 to 2027
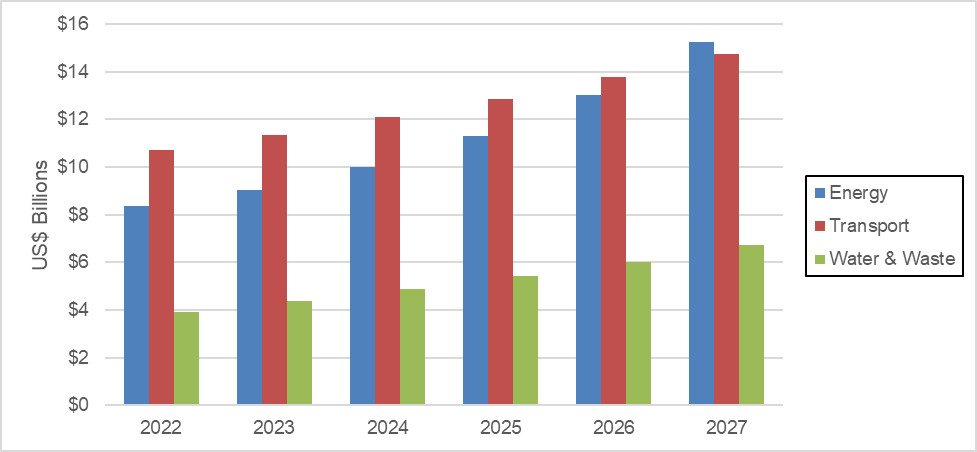
Learn some other industrial cybersecurity trends in our technology trends paper.
Keeping IoT Devices Safe
As manufacturers and industrial players continue to deploy more Internet of Things (IoT) devices, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) providers and Certificate Authorities (CAs) are constantly updating their offerings. Much of the current focus is on automated provisioning because automation can free up resources for Information Technology (IT) teams. Manufacturers and industrial firms that adopt IoT devices should prioritize modular and scalable solutions, so PKI providers and CAs are scheming how to maximize profits in this growing market.
Car manufacturers, Tier One suppliers, telcos, and insurance companies show a keen interest in data security in telematics. One of the telltale signs is the growing adoption of fleet management platforms that allow supply chain leaders to track their shipments end-to-end. The devices and networks required for in-vehicle telematics need reliable digital security solutions, so it’s no surprise that companies are turning to Embedded Subscriber Identity Modules (eSIMs), Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs), and HSMs.
Worldwide, electric utilities and energy suppliers have rapidly transitioned to smart metering. As a result, demand for device identity management solutions has given rise to significant on-premises investment in cybersecurity projects. Local regulation has been a key catalyst in the adoption of smart metering and the subsequent uptick in IoT security investment as utilities and energy suppliers are forced to adjust.
Telco’s Role to Play
The short-term chip shortage challenges are making Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card vendors reconsider their strategy. For many SIM card vendors, the business model has shifted from one focused purely on hardware revenue to one leaning into recurring revenue stemming from eSIM management platforms. Users of eSIM will be able to manage their devices OTA and without an interface.
The traditional removal SIM card market isn’t in any danger of being replaced anytime soon. However, its annual shipments will decline at a mild rate, while eSIM shipments grow.
With more devices being deployed on-premises, enterprises will seek reliable, low-latency connections. Telco operators will face immense demand from enterprises as they install secured 5G infrastructure that is optimized for their particular needs. Mass 5G adoption will also call for third parties, such as network equipment operators and digital security vendors, to provide their services.
Always Keeping the Guard Up
Enterprises in manufacturing and industry are at an inflection point as the world edges closer to becoming nearly 100% digital. It’s natural to be concerned about applications, devices, and network infrastructure being penetrated by bad actors. As Cybersecurity Ventures notes, cybercrime costs the world more than US$10.5 trillion annually. Without reliable digital security solutions, an existential crisis may be brewing for any unsuspecting company.
To better understand the current affairs of manufacturing and industrial cybersecurity, including key trends and market forecasts, download ABI Research’s The State of Cyber & Digital Security report.