Fiber optics are the apex of data transmission technologies. Using a flexible, transparent optical fiber constructed from silica, fiber optic cables leverage photons to pass network information at around 2/3 the speed of light. Being the fastest and most vigorous backhaul networking solution, Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) have made fiber optics a mainstay for supporting 5G deployments in the face of increasing networking needs of consumers and enterprise use cases. In this article, you’ll read about four high-bandwidth applications that would greatly benefit from fiber optics.
TVs and UHD Content
One of the biggest use cases for high-bandwidth fiber optics is for facilitating the smooth use of multiple Televisions (TVs), 4K, and 8K content. Video content consumes massive amounts of Internet traffic, accounting for 82% of total Internet traffic worldwide this year.
4K and other Ultra-High Definition (UHD) content requires about 3X the bit rate speed of HD TVs, and around 15X that of Standard Definition (SD). And when there are multiple devices being used simultaneously, the strain on the home network compounds. These network capacity constraints can lead to delayed load times, video buffering, latency, and network disconnect.
To maintain satisfactory network performance, many TV users must leverage fiber optic cables. The crucial advantage that fiber optics holds is its high bandwidth faculty. Fiber optics usually accomplishes up to 10 Gigabits per Second (Gbps) and can be transmitted up to roughly 100 Kilometers (km) without any boosts.
XR and Metaverse Applications
Fiber optics would be a good home networking match for immersive Extended Reality (XR) and metaverse applications, such as social media, video game streaming, and interactive video. These consumer applications put a substantial burden on home networks and have significant bandwidth needs. A TikTok user, for example, may consume more than 840 Megabits (MB) of data in just 1 hour.
Immersive applications involve data-intensive technologies like Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), live 360° video, and volumetric display. This typically requires a network throughput of 25 Megabits per Second (Mbps) or more and sub-50 Milliseconds (ms) latency. Here, fiber optic cables would shine.
Smart Home
Another consumer application that would benefit from fiber optic cables is the smart home, which will not stop its strong growth. Users can manage smart home applications remotely with external devices like tablets, laptops, and mobile devices.
While common smart home devices, such as doorbells, household appliances, plugs, and lights usually don’t consume more than 1 Gigabit (GB) of network data monthly, other applications are much more bandwidth-straining.
For example, Wi-Fi-connected cameras and voice control front end devices can connect to a cloud network and stream music, podcasts, or other online content that eats up a lot of data usage. Contingent on device settings and features, a smart camera alone can use up anywhere from 18 GB and 400 GB of data every month.
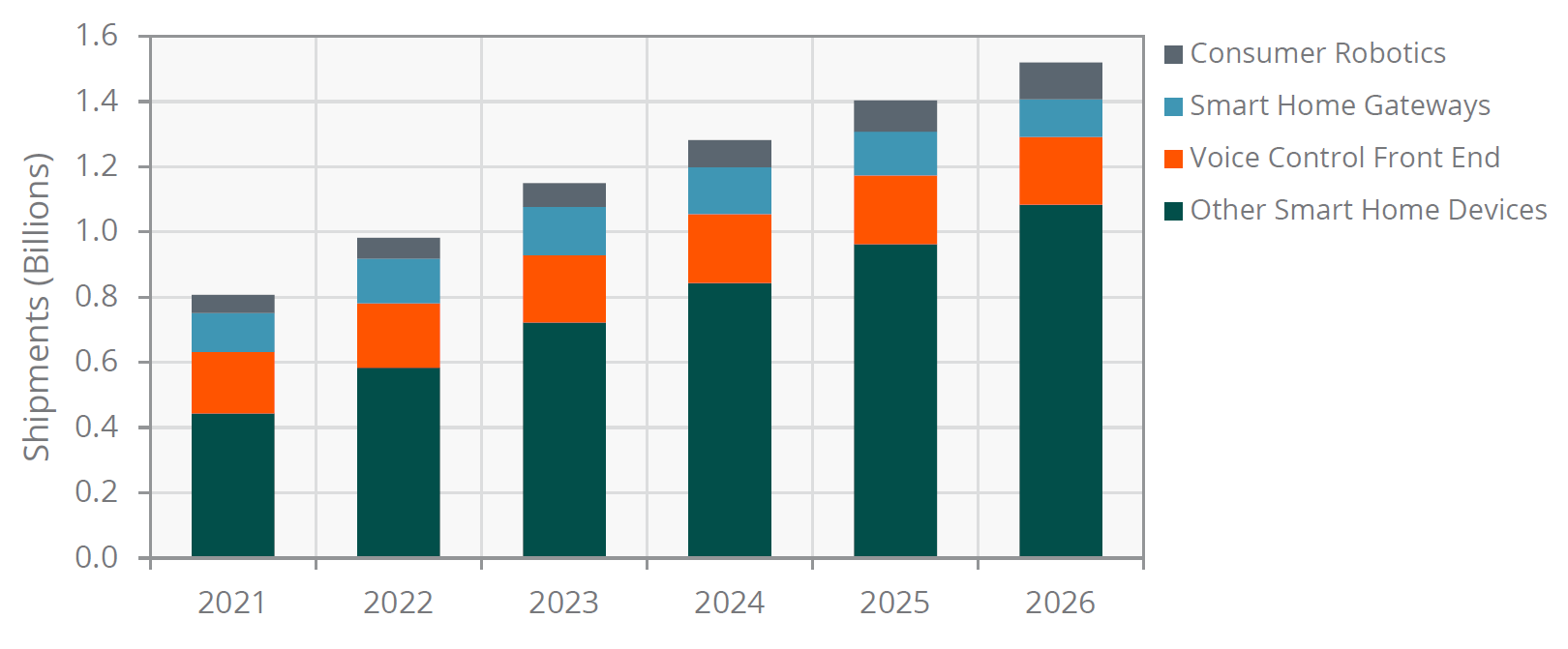
Consumer robotics is another bandwidth-intensive smart home application that consumes a huge amount of data and could introduce network deficiencies. As pointed out in Chart 1, with forecasts pulled from ABI Research’s Consumer Robotics and Smart Appliances market data (MD-HACRSA-103), these smart home categories are expected to only grow in popularity.
In 2026, we expect 1.5 billion consumer robotics and smart home devices to ship worldwide, nearly double the 807 million shipments in 2021.
Chart 1: Consumer Robotics and Smart Home Hardware Shipments: 2021 to 2026
Immersive Collaboration
Immersive collaboration, in the context of the enterprise metaverse, entails interactive cloud services and software, digital twins, simulations, video conferencing, virtual events, and virtual headquarters (HQ). As pointed out in the Enterprise Metaverse Implications for the Workplace, Virtual Events, Retail, and More Research Highlight, the immersive collaboration and digital twin/simulations market will be worth US$58.9 billion by the end of the decade—showcasing the increased adoption of immersive in the modern enterprise.
It goes without saying that these bandwidth-intensive applications, particularly video-centric applications, introduce more pressure on a company’s network. Indeed, office networks are increasingly requiring Gbps capabilities.
To illustrate, digital twins and simulation software necessitate the continuous collection of real-time data to be transmitted over the network using Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. These immersive solutions enable enterprise users to influence high-fidelity assets in real time, but these applications require demanding bandwidth and latency requirements (25 Mbps to 600 Mbps bandwidth and sub-30 ms latency).
In just 1 hour of work, an HMD user could consume up to 11 GB to 270 GB of data. Fiber optics backhaul, being the pinnacle of data transmission technologies, would be a good connectivity technology candidate here because it can handle Gbps applications.
Fiber-to-the-Commercial-Office (FTTCO) will be seen as a must-have networking solution that enables critical network and business activities. Therefore, in ABI Research's assesment, we believe the deployment of fiber infrastructure will be an integral aspect of the future modernized enterprise in both developed and developing markets.
Gain More Insight
Fiber optics are regarded as one of the most reliable networking solutions on the market, whether it’s for consumer usage or to support enterprise networks. As Internet traffic continues to climb significantly, fiber optic cables will increasingly be seen as a go-to solution to the interruption of high bandwidth applications.
To better help enterprise users and MNOs survey the importance of fiber optics in improving networks, download ABI Research’s The Role Of Fiber Optics In Your Network whitepaper.


