SIM Card Demand to Recover in 2024, but Slow Down After
Global Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card shipments were down -7.2% in 2023, reaching 4.09 billion units. This downward growth trend was primarily caused by reduced demand for consumer electronics devices and a stronger-than-expected impact of eSIM in the United States.
Although removable SIM card demand will bounce back with 4.19 billion shipments in 2023, ABI Research expects the market to consistently decline through the rest of the decade. As noted in a recent blog post, the increased use of Embedded SIM (eSIM) is a growing trend in the mobile markets. For example, our analysts expect 222 million fewer removable SIM card shipments in 2028 compared to our previous forecasts.
eSIM-only devices are expected to expand beyond U.S. borders, leveraged by consumers in Canada, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, China, South Korea, and Japan by 2026. Besides the consumer space heating up for eSIM, the upcoming SGP.32 specification will support more Machine-to-Machine (M2M)/Internet of Things (IoT) applications for eSIM. This latter development will drive significant eSIM growth in the enterprise/industrial sectors.
Most eSIM shipments will continue to come from consumer markets, including handsets, wearables, laptops, notepads, and tablets. However, with the SGP.32 specification, more M2M/IoT applications will be targeted for eSIM. Its predecessor, SGP.02, was primarily tied to automotive applications only.
Chart 1: SIM and eSIM Card Shipments, World Markets: 2022 to 2029
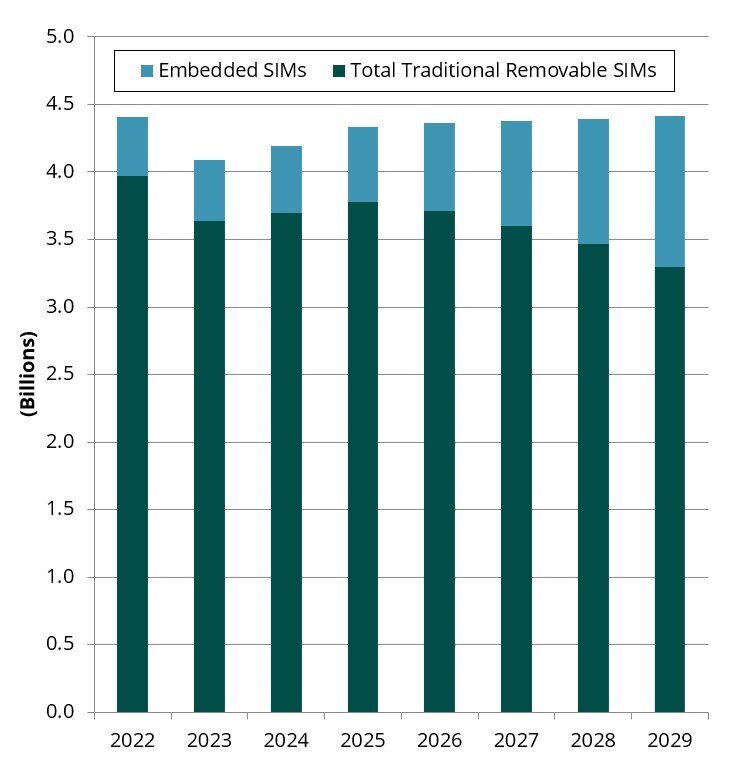
(Source: ABI Research)
Check out the Research Highlight, Embedded SIM (eSIM) Markets—Capitalizing on an Expanding Landscape for further a more recent analysis.
eSIM Market Amassing Strong Support
eSIM shipments were up 4.4% in 2023, reaching 457 million units across both the consumer and M2M/IoT segments. This year, ABI Research forecasts eSIM shipments to increase by 9.6%, surpassing the 500 million mark. Although there is currently limited support for eSIM in the M2M/IoT market, more device manufacturers will warm up to it once the SGP.32 specification is fully ratified.
Spearheaded by Apple, the consumer eSIM market is gaining traction, notably in the United States. All Apple smartphones sold in the United States now use eSIM-only, with expectations to expand and roll out eSIM in select European countries and key Asian countries like Japan and South Korea. On top of this, China will likely begin supporting eSIM within smartphones, making 2026 a critical year for the consumer eSIM market.
Samsung, although supporting it in flagship devices, has also shown an inclination to support eSIM within its mid-tiered smartphone selection, with eSIM being used for its A55, A54, and A35 smartphones. These vendors are expected to increasingly integrate 3-in-1 eSIM converged solutions that combine eSIM with Near Field Communication (NFC) and Secure Element (SE) functionality. Given Apple and Samsung’s respective success in the mobile wallets market, the addition of NFC and SE would be no surprise. Those applications require close proximity authentication and a high level of security.
While Apple supports eSIM across its entire smartphone range, most other Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) focus only on flagship devices. This is a key market inhibitor for eSIM, as mainstream consumers purchase mid-level devices.
eSIM in the M2M/IoT space has historically been limited to automotive use cases because the SGP.02 specification is tailored to the automotive industry. However, the incoming SGP.32 specification will be a breath of fresh air for the eSIM market as it targets broader IoT applications. The first Proof of Concept (PoC) connections for IoT eSIM will be seen in late 2024, and commercial launches are likely in 2025.
Chart 2: eSIM Shipments, World Markets: 2022 to 2029
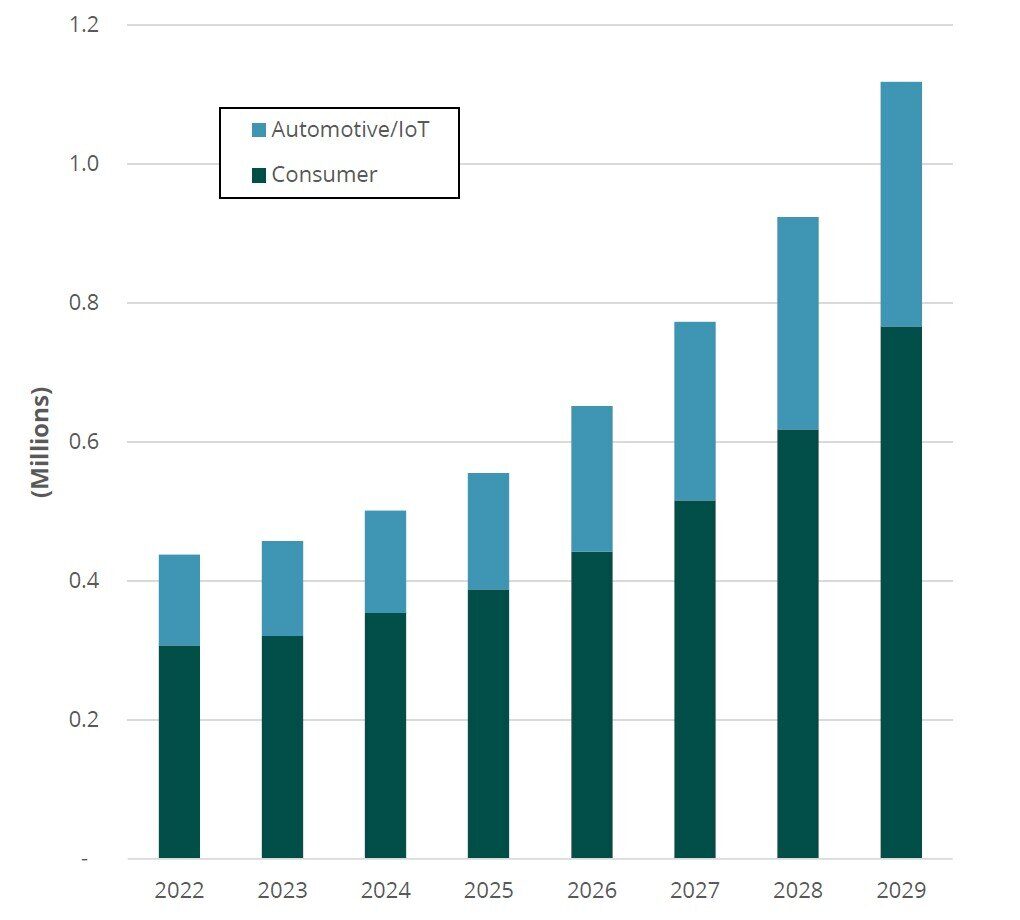
(Source: ABI Research)
How SIM Card Vendors Should Respond
The SIM card market is rapidly evolving, with new form factors being supported and industry dynamics shifting. Removable SIM will continue to be the most common type of SIM used in devices, but eSIM’s momentum cannot be ignored. With the market clearly gravitating toward eSIM-only, ABI Research believes SIM card vendors should take the following actions:
- Prepare for the Shift to eSIM Technology: The rapid adoption of eSIM, especially with Apple’s eSIM-exclusive smartphones in the United States, serves as a key example for SIM vendors. This insight can help them anticipate how eSIM-only devices might influence their removable SIM markets in other regions.
- Recognize the Resurgence of Pricing Pressures: Vendors must focus on balancing market share growth with strategies to protect margins. With aggressive competition from Chinese vendors in international markets, adopting a selective support strategy is essential to mitigating potential margin and pricing erosion.
- Track Developments Regarding SGP.32: While the standard awaits full ratification, the industry’s strong confidence suggests that developing pre-certified solutions poses little risk. Organizations with these solutions will have a competitive edge in transitioning to fully-certified SGP.32 solutions once available.
- Develop a Streamlined eSIM IoT Strategy: Forge partnerships with chipset and module vendors, Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs), Mobile Network Operators (MNOs), and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). Despite SGP.32’s intent to simplify IoT eSIM adoption, the process remains intricate, requiring diverse collaborations for effective enterprise deployment.
The content of this article is sourced from ABI Research’s SIM Card and eSIM Market Data Overview: 2H 2024. Download today!


