Challenges of the Telecom Regulations
|
NEWS
|
As the Internet of Things (IoT) industry is expanding, the demand for built-in internet connection is also growing. Previously, the connectivity of devices and machines was the responsibility of end users and service providers. Nowadays, such practices are becoming impractical; since IoT devices are shipped globally, the location change from country to country is a new reality. The ideal situation would be for IoT devices to have permanent international roaming, with no restrictions on connectivity and data transmission. In reality, the traditional telecom industry was not designed to support IoT; hence, there is a definite “catch-up” game in the area of best business practices and national regulations. The National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs) led by the European Union example are slowing, introducing the revision of the IoT roaming, connectivity, and IoT data laws. The European Union is leading the pack in introducing E.U.-wide permanent roaming, known as “Roam Like at Home,” which has provisions to regulate the Machine-to-Machine (M2M) space through the establishment of the Body of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC).
Despite existing benchmarking of E.U. regulations on the permanent roaming of IoT devices, the challenge of addressing regulations is much broader. The national regulations may not adequately describe practices and regulations concerning IoT, and there is the existence of industry-specific regulations, for example in automotive and energy. IoT connectivity regulations may fall under national monopoly/non-competitive practices or be inadequately regulated by protectionism and localization laws. Nonetheless, there is an apparent disparity in existing regulations, laws, and practices globally, which needs to be analyzed on a country-by-country basis to ensure the successful execution of the IoT connectivity business model.
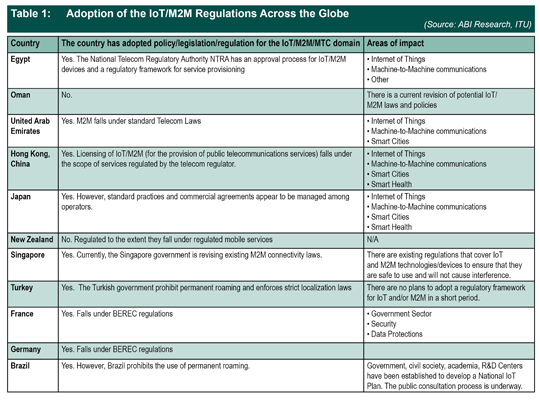
Country-Specific Adoption of the IoT/M2M Regulations
|
IMPACT
|
Interestingly, most of the NRAs are still viewing the IoT providers as somewhat “traditional” mobile providers. However, there is a dynamic for further differentiation between SIM and eSIM providers in the context of the same IoT cases, due to the utilization of telephone numbers. The table below showcases the disparity of IoT regulations across various nation states. The lack of harmonization, nevertheless, is expected to continue, as the level of service regulation varies dramatically:
National, Regional, and Continental Cooperation Models
|
RECOMMENDATIONS
|
IoT is playing an essential role in the developing and influencing sectors, such as health, transportation, education, and government, as well as at the industry level, by impacting logistics, manufacturing, production, and various other processes. The growing demand for IoT/M2M services in various industries requires a more significant technical, regulatory framework to be put in place since the devices/sensors/gateways continuously demand mobile connectivity and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) provisioning.
As the table above showcases, the different countries and regions are approaching the legislative framework differently, which makes the market highly heterogeneous. Although it is essential to acknowledge that the complexity of the market is shifting further due to the emergence of multilateral and bilateral regional roaming agreements, the examples of such cooperation can be summarized as follows:
- European Union and BEREC Cooperation Framework
- Associação de Reguladores de Comunicações e Telecomunicações da Comunidade dos Países de Língua Portuguesa (ARCTEL-CPLP): An association of Portuguese-speaking countries that facilitates knowledge sharing and the adoption of best practices and harmonization of regulation in the communications sector among various NRAs.
- Southern African Development Community (SADC): A regional initiative to enable the environment with affordable and competitive mobile roaming services. In March 2015, the Communications Regulators’ Association of Southern Africa (CRASA)’s Roaming Task Team (CRTT) was established to assist CRASA in implementing the ministerial directives.
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) International Roaming Regulatory Initiative: The regional body received the mandate from the GCC telecommunication ministers committee to manage the issues of International Mobile Roaming (IMR) pricing to achieve harmonization and standardization in the region. Such an initiative is expected to expand toward the IoT and M2M domain.
- The Caribbean Telecommunications Union (CTU): Established in 1989 to coordinate/harmonize telecommunication policy development alongside the Eastern Caribbean Countries Commission (OECS) and Eastern Caribbean Telecommunications Authority (ECTEL), CTU’s current mandate covers roaming regulation, licensing, and authorizations.
While assessing the level of national legislation in combination with regional and sub-regional regulatory initiatives alongside International Telecmmuniation Union (ITU) and GSMA regulatory directives, it became apparent that regulatory vacuums and a high degree of uncertainty during the time of reactionary changes restrict the expansion of the IoT/M2M business model. The fast-developing variety and volume of the IoT/M2M applications, combined with regulatory uncertainty over permanent roaming scenarios, illustrate the need for global-level standardization, continuous monitoring, and case-by-case evaluation of newly emerging IMR regulations. Therefore, further discovery and global cooperation concerning permanent roaming in the IoT/M2M context will be beneficial.