Recovery of VC Activities in 2021
|
NEWS
|
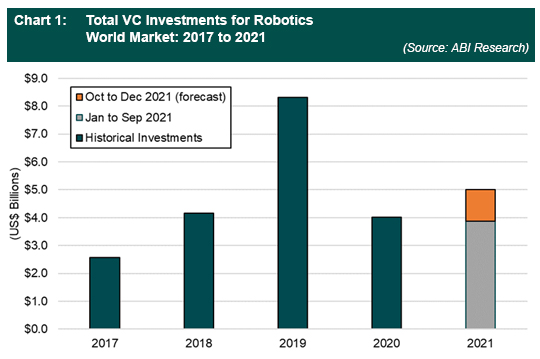
The year 2020 was a confounding year for robotics. On the one hand, the COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically accelerated the deployment of robotics solutions. As a result, Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) and Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (SUAS) vendors have reported an uptick in sales revenues due to wide-scale adoption and deployment of their products. Such products have been deployed for autonomous material handling, disinfection, crowd management, and last-mile delivery. On the other hand, Venture Capital (VC) funding dropped significantly in 2020. After hitting a historical high in 2019 with US$8.3 billion (total not inclusive of self-driving vehicles and related technologies, such as processor and mapping), total funding suffered a 52% decline, resulting in a total of only US$4 billion in 2020. This figure is even lower than the U$4.2 billion raised in 2018.
Fast forward to September 2021 where the robotics VC market is currently showing a strong sign of recovery. The total investment from January to September has reached US$3.8 billion. In comparison, US$2.7 billion VC funding was raised in the same period in 2020. ABI Research estimates that the total VC investment could reach US$5 billion by the end of 2021—not a historical high, but a clear sign of confidence.
Key Trends and Players
|
IMPACT
|
The year 2019 is known as the year of surgical robots, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and AMRs. Cainiao Smart Logistics, Nuro, Ocado, Postmates, and Geek+ all raised more than US$150 million each while Fetch Robotics, Locus Robotics, Gecko Robotics, and Starship Technologies were not too far behind. The market anticipated large-scale adoption of AGVs and AMRs across various sectors, with last-mile delivery being one of AMR’s most anticipated use cases.
In comparison, the VC market of 2020 and 2021 has had a slightly different focus. Surgical robots—in companies such as CMR Surgical, ZAP Surgical Systems, PROCEPT BioRobotics, and Neocis—and AMR technology—in companies such as Nuro, HAI Robotics, Seegrid, and Vecna Robotics—remain as key focus areas. Still, other startups that received VC funding have revealed other intriguing development trends that demonstrate new focal points in the robotics industry as follows:
- The Emergence of Disinfection and Cleaning Robots: COVID-19 has validated the importance of disinfection and cleaning robots. Shenzhen Pudu Technology and Gaussian Robotics raised US$155 million and US$100 million respectively in 2021. Shenzhen Pudu Technology has launched Puductor 2, an AMR that is equipped with ultrasonic dry mist and ultraviolet light disinfection and that starts as a delivery and reception robot. Gaussian Robotics, for its part, has developed a wide range of cleaning robots, including scrubbers, sprayers, sweepers, and vacuum robots. These robots have been deployed in many markets, including Singapore, Thailand, and Russia.
- More Attention on SUASs: The wide-scale adoption of drones has brought a lot of scrutiny on the dominance of Chinese vendors in this sector. The China-U.S. trade dispute and the National Defense Authorization Act have led to further decoupling of the supply chain, forcing non-Chinese drone developers such as U.S.-based Skydio to come up with alternative solutions. Skydio’s fully automated drones are uniquely differentiated from major drone vendors that focus on remote control.
- Software for RoboOps: Increasingly, as robots make their way to more end users, there is a push toward making robot programming, onboarding, and monitoring more approachable and seamless as not every end user has strong robotics expertise. Low-code or even zero-code solutions are essential to encourage wide-scale adoption. For example, Mech-Mind Robotics and Realtime Robotics have developed zero-code machine vision software for various manufacturing and warehousing tasks, such as depalletizing, machine tending, order picking, defect detection, and size measurement. Rapid Robotics offers an end-to-end Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) solution that features an easily programmable and configurable industrial robotics arm designed to handle all the previously mentioned tasks.
A Growing Market with a Rich Ecosystem
|
RECOMMENDATIONS
|
A common trend among developed and emerging markets is to tailor products for the older population. COVID-19 has further accelerated the need for automation. What is even more critical in automation are maturing robotics hardware and software technologies. Many pure-play software startups have, in recent years, developed common platforms for robotics development, programming, fleet control and management, data analytics, deployment, and onboarding. Open Robotics has been actively supporting robotics deployment via Robot Operating System (ROS) 2 and its frequent software updates. In addition, prominent computing processor vendors like Qualcomm and Xilinx have released robotics-specific processors that feature native ROS 2 support. Intel did rock the robotics industry by announcing the retirement of its influential RealSense camera products. Still, the company walked back from the announcement and clarified that it is only retiring a selected number of products.
In addition, consolidation remains a big theme, especially as the industry saw several key acquisitions in 2020 and 2021. Larger robotics companies are eyeing prominent robotics startups to strengthen their internal capabilities. Industrial giant ABB Robotics acquired Codian Robotics and ASTI Mobile Robotics to venture into the logistics and warehousing sector. Ocado, which has developed its own warehousing system, acquired Haddington Dynamics and Kindred Systems, thereby expanding its existing product line. Locus Robotics, a successful RaaS vendor for goods-to-person robots, went in a different direction by acquiring Waypoint Robotics, an AMR vendor focusing on material handling. Not wanting to be left behind, nonrobotics solution providers Zebra Technologies and JASCI Software also acquired AMR vendors Fetch Robotics and NextShift Robotics respectively in 2021, with the aim of diversifying their product offerings further.
As 2021 comes to a close, the robotics investment market has finally become vibrant again. The robotics industry has taken another big step by moving from niche high-end solutions to become more fully integrated with regular tasks and workflows in the workspace.
