Manufacturers are expected to spend more than US$1 billion on private 5G in 2025. Growing at a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 45.7%, that number will surpass US$8.7 billion by 2030.
Why such a rapid uptake in 5G networks in the manufacturing sector? The short answer is operational survival.
In recent years, manufacturing companies have contended with a global pandemic, high inflation, soaring energy costs, labor shortages, supply chain complexities, and intensified geopolitical tensions. These challenges have eaten away at manufacturers’ production and quality control capabilities. To get back on track and maintain profit margins, manufacturers have increasingly invested in Industry 4.0 technologies that automate tasks and provide operational visibility. This digital transformation inevitably necessitates reliable connectivity for industrial applications to run smoothly. While several connectivity options are available, a private 5G network stands out as an essential solution. Industrial 5G offers manufacturers the low latencies, enhanced security, and high bandwidths that smart factories require and legacy solutions cannot accommodate.
Chart 1: Private 4G and 5G Revenue in Manufacturing, World Markets: 2024 to 2030

Although Wi-Fi and wired connections like Ethernet are the go-to means of connecting manufacturing operations today, they have notable shortcomings. For example, although Wi-Fi is a well-established industrial connectivity technology, it lacks reliability, fast handovers, and robust communication required for mission-critical applications. Fixed connections are also a liability, as they require the expensive task of physically connecting machines and sensors to specific points within a facility. As a result, using wired connections is not a cost-effective way to expand a production plant or add new connected systems. Instead, manufacturers should consider investing in a private 5G network or at least combining cellular with other connectivity technologies.
To better understand how industrial 5G fits into the smart manufacturing discussion, I will answer four key questions weighing on the minds of industry stakeholders.
Table of Contents:
- How Does Private 5G Improve Manufacturing Processes?
- What Security Advantages Can You Expect with 5G?
- Is a Private 5G Network Future-Proof?
- What Is the Anticipated Return on Investment for Private 5G?
The video below is a one-minute guide on how 5G can enhance your manufacturing operations.
How Does Private 5G Improve Manufacturing Processes?
5G features such as Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC) provide substantial operational efficiency, productivity, and safety gains for manufacturers. These 5G capabilities, in combination with deterministic networking, enhance existing Industry 4.0 use cases like Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and asset tracking, while supporting novel applications yet to be deployed.
ABI Research has held discussions with a number of manufacturers about their private 5G experience. They report the following benefits:
- Up to 30% productivity improvements by minimizing downtime and optimizing operations
- Up to 20% energy savings from high-efficiency operations
- Up to 25% to 30% maintenance cost reductions, spurred by predictive and preventative maintenance
- More than a 40% decrease in workplace accidents because 5G supports robust safety measures like real-time equipment monitoring
Figure 1: 5G Capabilities in Manufacturing
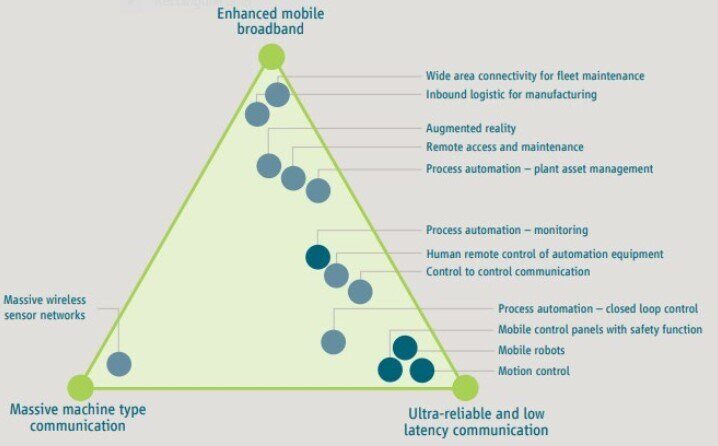
(Source: ABI Research)
What Security Advantages Can You Expect with 5G?
A recent survey conducted by ABI Research and the Digital Manufacturing and Cybersecurity Institute found that improved security was the top reason why U.S. manufacturers invested in private 5G. Private 5G’s low latencies and real-time network monitoring capabilities provide a layer of security not seen with other wireless and wired networking solutions.
Deploying a private cellular network provides manufacturers with many more network protection mechanisms than Wi-Fi and other networking solutions. For example, only users with a specifically designed Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card are granted access to the 5G network. This extra level of security prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data. Moreover, industrial 5G enables manufacturers to install all connectivity infrastructure on-premises. Keeping infrastructure local, in tandem with traffic filtering mechanisms, ensures that sensitive networking data doesn’t fall into the wrong hands on a public network.
Chart 2: Private 5G Investment Drivers for Manufacturers
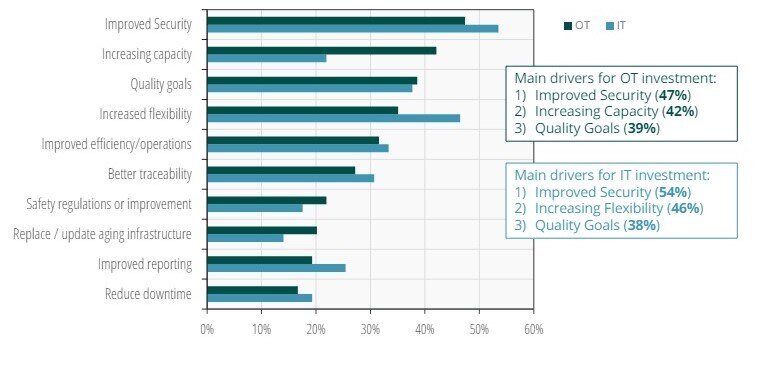
(Source: ABI Research)
Is a Private 5G Network Future-Proof?
A private 5G network is built for the future of industrial operations, providing unprecedented scalability and flexibility. As manufacturers deploy more Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, robotics, and other Industry 4.0 technologies, 5G is ready to handle their connectivity requirements.
Furthermore, 5G features like URLLC will be essential for mission- and safety-critical use cases in manufacturing operations. While URLLC and other features are not driving private 5G adoption today, they will be instrumental for any future enterprise use cases. Below are several notable use cases that private 5G will unlock for manufacturing companies.
- Real-time surveillance and monitoring of the production line
- Remote access to IoT devices
- Automated emergency alerts that are sent to devices and personnel within the facility
- Remote control of safety-critical systems (e.g., ventilation, circuit breaker, etc.) for swift response during emergencies and power outages
Additionally, private 5G architecture is designed with adaptability in mind so that manufacturers can fine-tune the network to their unique operational needs. Manufacturers can also leverage private 5G network slicing to modify network size and performance without deploying new infrastructure.
Achieving significant levels of network agility requires manufacturing companies to invest in network management software solutions. This software aids manufacturers in scaling the network and introducing new connected devices. Once supported with these tools, the 5G network will accommodate future industrial applications and use cases.
What Is the Anticipated Return on Investment for Private 5G?
Now, to answer the question you’ve been waiting for: what kind of Return on Investment (ROI) can private 5G generate for your manufacturing plant? The recent ABI Research whitepaper, Unlocking the Value of Industry 4.0, gives us a good idea of what to expect.
As reported in the paper, my team and I conducted an exercise forecasting the measurable results of a U.S.-based electronics manufacturer adopting private cellular-enabled Industry 4.0 technologies. After 5 years, a manufacturer with a 200,000 Square Meter (m2) smart factory can expect the following:
- A 7.6% increase in gross profit
- Operational cost savings of US$1.05 billion
- An ROI of US$49.3 for every US$1 spent
The main drivers of the 5G-supported benefits include the use of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), improved inventory management, and condition-based monitoring.
A key factor we evaluated in the study was the Cost of Inaction (COI)—the opportunity cost of not deploying a private 5G network at the plant. Our study found that a U.S.-based electronics manufacturer would miss out on an additional 1.19 million units being produced. That equates to US$1.03 billion in extra revenue going down the drain.
ABI Research conducted other studies on a Japanese electronics manufacturing plant and German and South Korean automakers. While not as impressive as the example of a U.S.-based electronics manufacturer, these other companies are looking at increased gross profit margins of between 4.9% and 7.1%.
Next Steps
This blog post answered some of the most vital questions surrounding private 5G in manufacturing. While the benefits, capabilities, and profitability of industrial 5G have been covered, the next step is to outline an optimal approach to deployment. Moreover, you should identify the manufacturing use cases a private 5G network can improve or bring to life. For a complete discussion on 5G’s role in the future of smart manufacturing, download ABI Research’s free whitepaper, Private 5G Drivers & Use Cases in Manufacturing.


